Did you know that you can navigate the posts by swiping left and right?
Reducing CareShare Load Time: 1+ Mins To 1 Sec
08 Oct 2020
.
6 mins
:
learning
.
Comments
#work
#bug fix
#programming
#guide
#experience
#devops
#tech
#careshare
#zealth-ai
How fast a website loads and lets the user interact is one of the key parameters that shape customer retention. At Zealth-AI, we are working on our product, CareShare, to ease the lives of COVID patients and we observed, with a large set of functionalities, the load time was increasingly becoming a problem. This was more pronounced for us as we are mobile-focused and most of our patients belonged to areas with poor connectivity - leading to higher drop-offs.
Old Setup & Issues
We were using Firebase hosting to serve our website; the same website is presented as a webview in our mobile application.
WebView is a system component powered by Chrome (or equivalent engine on iOS) that allows apps to display web content.
Firebase hosting claims to have (see below image taken from Key Capabilities of Firebase hosting) a Content Delivery Network (CDN) which should be caching our static content and serving it faster - it didn’t happen in our case. Most of the time, all the caching that was being done (or so it seemed) was on the browser level and a hard refresh lead us to an irritatingly slow loading which would take minutes. We tried to fiddle around with Firebase settings to no avail as no controls or information about the inbuild CDN are provided.

Observing the network load time and what was being loaded for rendering the website content, it was evident to us that we were also loading a few unused or unoptimized scripts. Adding to our woes, these scripts would sometimes push the loading of crucial scripts to a later time and make interactivity of the website poor.
In a gist, the issues leading to slow loading times were:
- No CDN backing and caching of static content.
- Serving unoptimized or non-minified JS and CSS.
- Serving unused JS and CSS.
Minification (minify / compress / ) is the process of compressing code from the original size to the smallest size by removing whitespace characters, shortening variables names, etc.
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a highly-distributed platform of servers that helps minimize delays in loading web page content by reducing the physical distance between the server and the user and caching it close to them.
How We Solved It
After identifying the key problems, we targeted each of the them separately:
- Added a Cloudflare CDN layer between clients and firebase hosting.
- Minified all JS and CSS (solved by Cloudflare).
- Removed unnecessary JS and CSS imports.
Adding Cloudflare
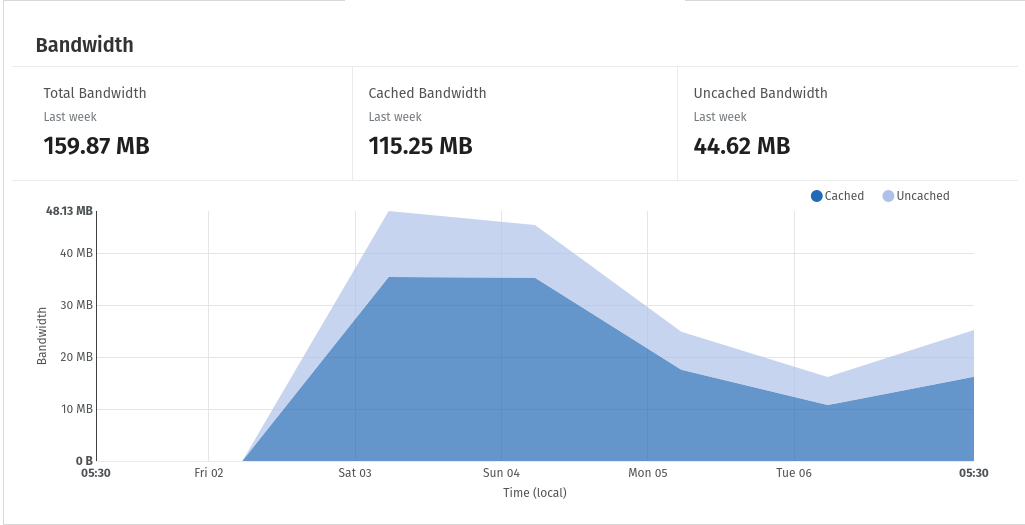
Adding a Cloudflare layer between the clients and our firebase hosting is one of the most effective steps that resolved our issues. The caching provided by Cloudflare is very strong and, since we do not frequently update most of the static content, the cached content served is very high (>72%) and this is just within the first week!
The article Why You Should Put a CDN Like Cloudflare in Front of Firebase by Geoffrey Bourne highlights the key advantages of using Cloudflare in general. Here are the benefits that we are getting after using the CDN apart from the blazing fast load times.
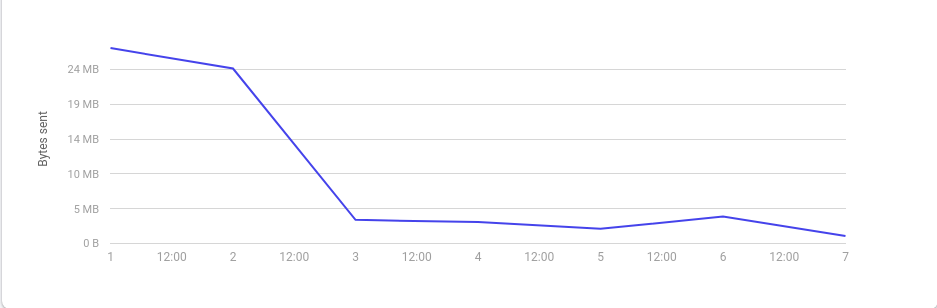
- In our case where we do not update the website very frequently, our firebase hosting download footprint has decreased by roughly 90% (from avg. 26 MB to 2.4 MB). This has directly impacted our firebase hosting billing, and now we have to pay 90% less.
- It automatically minifies our JS, CSS, and HTML (yay, bonus!) and then serves the optimized smaller versions instead of the original ones. This saves us the hassle of minifying the files ourselves that had the overhead of working on non-minified files and then minifying them before committing our work.
Removing Unused JS & CSS
This was a tricky change to make - although we knew that not all the scripts and styling components are being used, it was difficult to pinpoint, remove, and test that the website was working correctly. For solving the issue, we followed the following steps for every JS/CSS file.
- Read what is the purpose of the script and associate it with elements available on the page.
- Check if it’s slowing down the website - if it was in the top 10 scripts taking the highest time to load (using networks tab in Brave’s DevTools).
- If the script was slowing down the website we would disable and check functionalities it could break (learned from step 1).
- If it was non-breaking, remove the import. If it is breaking, move it to load at the end and make the load asynchronous.
// loading js asynchronously in HTML
<script src="demo_async.js"> async</script>
Results
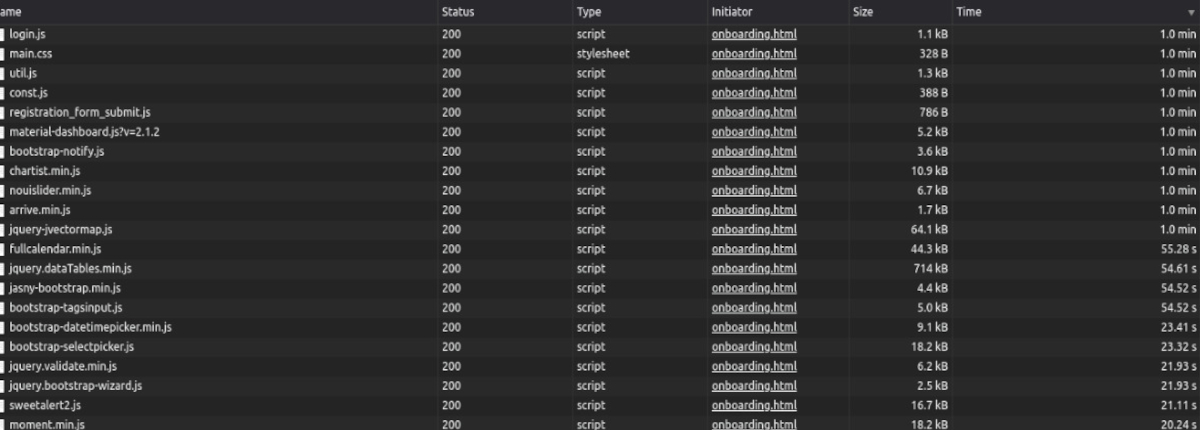
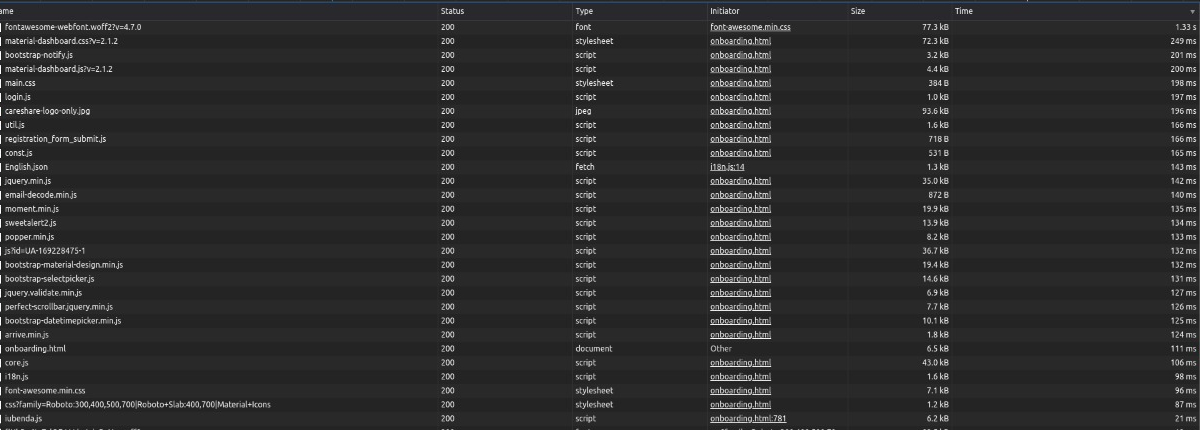
With a series of incremental changes - both in how we are serving the website and what we are serving, we managed to bring down the average load time from several minutes (first image below) to a little more than a second (second image below).
Conclusion
Initially, we were skeptical if Cloudflare would be solving our problems or not, and it turned out to be the most significant difference-maker. The free version of Cloudflare is more than enough for general purpose usage and caching with flexible controls; the high cost savings (in hosting) of more than 90% that we are getting now is a cherry on the cake.
We are not satisfied with my approach on how we removed the extra JS & CSS imports and it was the best we could come up with within the limited time. We are looking to find new ways or tools that are scalable, please share in the comments if you have any ideas or experience.
